Have you ever wondered where the air we breathe and the food we eat come from? Well, a big part of that answer lies in something called the carbon cycle. Learn about the steps of the carbon cycle, and why it is so important for life on earth.

What Is The Carbon Cycle?
Here is a simple carbon cycle definition for kids:
The carbon cycle is like a natural recycling system for an essential element called carbon. Carbon is an important part of the air, the ground, and all living things. It moves around in a circle, changing from one form to another.
Plants use carbon dioxide from the air to make food, and animals eat the plants to get energy. When plants and animals breathe or when things like wood burn, they release carbon dioxide back into the air. This process helps keep the air and Earth’s ecosystems balanced.
Let’s explore the steps of the carbon cycle in more detail below.
Also, learn about the nitrogen cycle for kids!
Free Carbon and Nitrogen Cycle Activities
Grab this printable carbon cycle and nitrogen cycle activity pack to add to your lessons!

The Steps Of The Carbon Cycle
These steps demonstrate how carbon cycles through living organisms, the atmosphere, oceans, and soils, maintaining a delicate balance that affects all life on earth. Here are the basic steps of the carbon cycle:
Photosynthesis
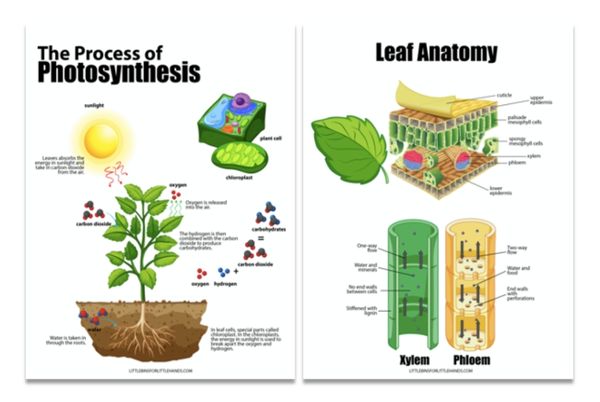
Plants take in carbon dioxide from the air and use sunlight to turn it into food (glucose) for themselves. During this process, oxygen is released into the air as a byproduct. Grab the printable photosynthesis worksheets to learn more.
Consumption
Animals eat plants (or other animals that have eaten plants) in a food chain, and in doing so, they take in the carbon that the plants have stored.
Respiration
Animals breathe (respire), which means they take in oxygen from the air and release carbon dioxide back into the atmosphere.
Decomposition
When plants and animals die, their remains break down. During this decomposition process, carbon is released back into the soil and air.
Fossilization
Over long periods, some carbon-containing remains of plants and animals become fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, which are stored deep within the Earth’s crust.
Combustion
When things like wood or fossil fuels (coal, oil, and natural gas) burn, they release stored carbon into the air. This happens when we use cars, burn wood in a fire, or use electricity from power plants that burn fossil fuels.
Ocean Uptake and Carbon Sink
The oceans absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, acting as a massive carbon sink. This absorption helps to regulate the amount of carbon in the atmosphere. However, too much absorption can lead to ocean acidification, which can harm marine life. See our ocean acidification experiment.

Why Is The Carbon Cycle Important?
Why is it so important to maintain the balance of carbon in the atmosphere and on earth? The carbon cycle is critically important and here’s why:
Regulation of Atmospheric CO2 Levels
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, which means it traps heat in the Earth’s atmosphere. The carbon cycle helps regulate the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Plants and trees absorb CO2 during photosynthesis, reducing its concentration. On the other hand, processes like respiration and combustion release CO2 back into the atmosphere. This balance in the atmosphere is crucial for preventing excessive global warming and maintaining a stable climate.
Oxygen and Food
Plants absorb CO2 from the atmosphere and, with the help of sunlight, convert it into food for growth. This process not only contributes to the planet’s oxygen production but also provides a food source for many other living organisms.
Carbon Storage
The carbon cycle involves the movement of carbon between different storage areas, including the atmosphere, oceans, and land. Some carbon is stored for long periods in forests, soils, and fossil fuels. This storage helps regulate the carbon concentration in the atmosphere and prevents it from accumulating excessively.
Healthy Soil
Carbon is an essential component of organic matter in soil. Organic matter improves soil structure, water-holding capacity, and nutrient availability. The carbon cycle contributes to the cycling of nutrients through decomposition and nutrient release, which supports healthy plant growth.

Energy Transfer
Carbon compounds store and transfer energy through various processes. This energy flow is essential for sustaining life on earth. Carbon compounds are part of the molecules that make up living organisms, such as proteins, fats, and carbohydrates.
Global Nutrient Cycling
Carbon is linked to other essential nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus. These cycles contribute to nutrient availability and overall ecosystem health. Learn more about the nitrogen cycle here.
The Role Of Plants In The Carbon Cycle
Plants play an important role in the carbon cycle as they are integral to both carbon dioxide uptake and the movement of carbon through various stages of the cycle. Here’s how plants are important in the carbon cycle:
- Through a process called photosynthesis, plants absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere and produce glucose (a simple sugar) and oxygen. This process takes place in chloroplasts, the organelles within plant cells. Learn more about plant cells.
- Plants store carbon in various parts of their structure, including stems, leaves, branches, and roots. Some plants, like trees, can store a lot of carbon over long periods.
- Plants can capture and store carbon from the atmosphere in long-term sinks. Forests, grasslands, and other vegetation act as carbon sinks by absorbing more carbon through photosynthesis than they release through respiration.
- When plants die or shed leaves, they release stored carbon through decomposition. The plant material breaks down, releasing carbon dioxide and other nutrients back into the soil and atmosphere.
- Plants help stabilize soils and prevent erosion. Erosion can transport organic matter containing carbon from the land into bodies of water. When these sediments settle, they can store carbon for extended periods, contributing to the overall carbon cycle. Learn more about erosion.
Overall, plants play a vital role in the carbon cycle. They influence carbon dioxide levels in the atmosphere, support the growth of ecosystems, and help to regulate Earth’s climate.
How Human Activity Affects The Carbon Cycle
Human activities have had a significant impact on the carbon cycle, primarily through the release of large amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These emissions disrupt the natural balance of the carbon cycle and contribute to global climate change.
Burning Fossil Fuels
The combustion of fossil fuels (such as coal, oil, and natural gas) for energy production, transportation, and industrial processes releases huge amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere.
This extra CO2 was previously stored underground for millions of years and is now being rapidly reintroduced into the atmosphere, leading to a rise in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
Deforestation
Clearing forests for agriculture, urban development, and logging reduces the number of trees and plants that can absorb CO2 through photosynthesis. This contributes to higher atmospheric CO2 levels because there are fewer trees to capture and store carbon.
Industry
Certain industrial processes release carbon dioxide as a byproduct. For example, cement production involves the release of CO2 during the chemical reaction that converts limestone to cement. Other manufacturing processes can also lead to the release of greenhouse gases.
Farming
Agricultural activities, such as plowing and tilling, can disturb soil and accelerate the decomposition of organic matter, leading to the release of CO2 into the atmosphere.
Livestock farming, particularly cattle, produces methane (CH4), another potent greenhouse gas, through the digestive processes of animals.
Burning Waste
Burning of waste materials, including plastics, releases CO2 and other pollutants into the atmosphere. This contributes to the atmospheric carbon burden and can have negative effects on air quality.
All together, these human activities have sped up the release of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, leading to global warming and climate change. The increased concentration of these gases traps heat, causing shifts in weather patterns, rising temperatures, sea level rise, and other environmental impacts.
Tips For Teaching Kids About The Carbon Cycle
Teaching kids about the carbon cycle can be a fun and engaging experience. Here are some simple and creative ways to make these concepts easier to understand for kids.
1. Hands-on Activities
Use hands-on activities to illustrate the cycles. For the carbon cycle, you can have kids act out photosynthesis with one child being the sun, others being plants, and another being carbon dioxide. They can then demonstrate how plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen.
2. Visual Aids
Use colorful posters, diagrams, or videos that depict the cycles in a child-friendly manner. Visual aids can help kids grasp the different steps involved and how carbon moves through the cycle.
3. Nature Walks
Take kids on a nature walk and point out elements of the carbon cycle in the environment. Show them plants, trees, and explain how they take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen. Look for signs of decomposition like fallen leaves and explain how it releases carbon into the atmosphere.
4. Experiments
Conduct simple experiments that demonstrate aspects of the carbon cycle. For example, you can grow a small plant in a closed container and explain how it recycles carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and respiration.
Try: Grow plants in mini greenhouse

5. Use Analogies
Analogies can help kids relate complex concepts to things they are familiar with. For example, you can compare the carbon cycle to a “food chain” where each step represents a part of the cycle.
6. Art and Crafts
Encourage kids to create art or crafts related to the carbon cycle. They can draw or make collages showing the different steps or create a mobile representing the carbon cycle.
7. Discussion
Engage kids in discussions about the carbon cycle. Ask them questions, encourage them to ask questions, and have group discussions to reinforce their understanding.
TIP: Remember to use age-appropriate language that suit your kids’ level of understanding. Making the learning experience interactive and enjoyable will not only help them grasp the concepts better but also foster a love for science and the environment.
Related Activities
- Food Chain Activity
- Photosynthesis
- Nitrogen Cycle
- Carbon Footprint
- Beach Erosion Experiment
- Soil Erosion Model
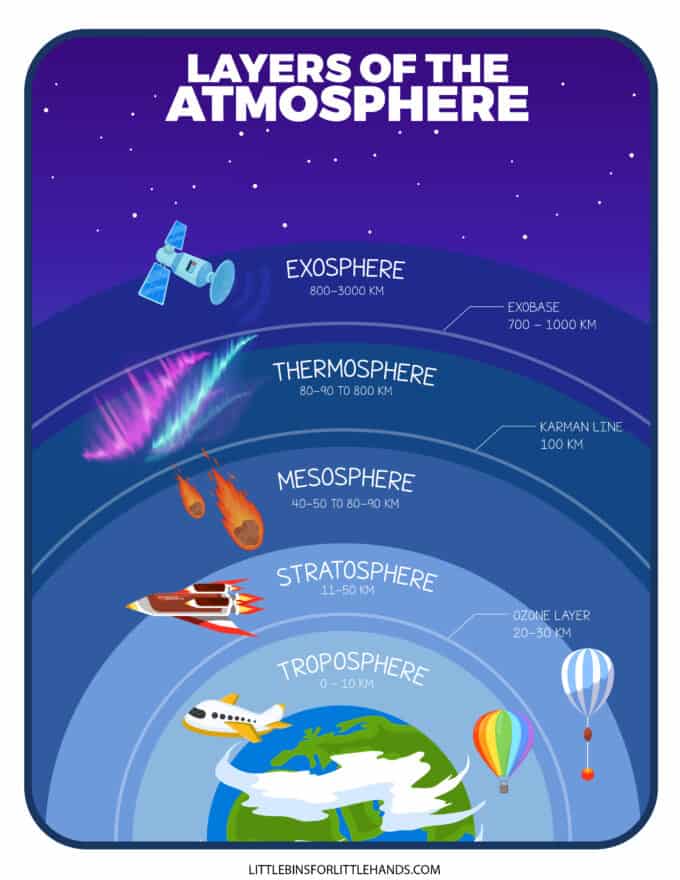
- Layers of the Earth
- Layers of the Atmosphere
Printable Science Projects For Kids
If you’re looking to grab all of our printable science projects in one convenient place plus exclusive worksheets and bonuses like a STEAM Project pack, our Science Project Pack is what you need! Over 300+ Pages!
- 90+ classic science activities with journal pages, supply lists, set up and process, and science information. NEW! Activity-specific observation pages!
- Best science practices posters and our original science method process folders for extra alternatives!
- Be a Collector activities pack introduces kids to the world of making collections through the eyes of a scientist. What will they collect first?
- Know the Words Science vocabulary pack includes flashcards, crosswords, and word searches that illuminate keywords in the experiments!
- My science journal writing prompts explore what it means to be a scientist!!
- Bonus STEAM Project Pack: Art meets science with doable projects!
- Bonus Quick Grab Packs for Biology, Earth Science, Chemistry, and Physics










