Chemistry is the branch of science that focuses on the study of matter, which is everything that takes up space and has mass. It explores the properties of substances, how they behave, and how they can change. Chemists are like detectives who investigate the natural world at the molecular level to uncover its secrets.

What is the History of Chemistry?
The study of chemistry has a long and interesting history that dates back thousands of years. Ancient Greeks were some of the first people to ask questions about matter and its properties. They believed that everything was made up of four elements: earth, air, fire, and water. However, it was not until the modern era that chemistry began to develop as a science.
What Are Areas of Chemistry?
Chemistry is a vast field that can be divided into several main branches. Let’s explore a few of them:
Organic Chemistry
This branch focuses on studying carbon-based compounds, which are the building blocks of life. Organic chemistry helps us understand how living things work and how we can create new medicines and materials.
Inorganic Chemistry
Inorganic chemistry deals with the study of non-carbon compounds. It helps us understand the properties of minerals, metals, and other substances that are not directly related to living organisms.
Physical Chemistry
Physical chemistry combines the principles of physics and chemistry. It investigates the behavior and properties of substances at the molecular and atomic level. Physical chemists study things like energy changes, rates of chemical reactions, and the interaction between matter and energy.
Analytical Chemistry
Analytical chemistry involves the analysis of chemicals and the identification of their components. Analytical chemists use various techniques and instruments to determine what substances are present in a sample and how much there is.
Environmental Chemistry
Environmental chemistry explores the impact of chemicals on the environment. It helps us understand how pollutants affect ecosystems and develop ways to protect and preserve our planet.
Learn More: Examples of Physical Change
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Chemistry is all around us, even in our everyday lives. Here are a few examples:
Color Changes
Have you ever seen a flower change color or noticed how food changes when cooked? These are all examples of chemical reactions that occur due to changes in the arrangement of atoms and molecules.
Pharmaceuticals
Chemistry plays a crucial role in the development of new medicines. Pharmaceutical companies use chemistry and chemical processes to create drugs to cure diseases or relieve symptoms.
Cleaning Products
Many cleaning products we use at home contain chemicals that help remove dirt and stains. Modern chemistry helps us understand how these substances work and how to use them safely.
Cooking or Baking
We use chemical reactions to transform ingredients into delicious meals when we cook. Baking, for example, involves chemical reactions that cause the dough to rise and become fluffy bread. Try our bread in a bag science project.
Learn More: Examples of Chemical Change
Who Is Marie Curie?
Marie Curie was a famous scientist who made groundbreaking discoveries in the field of chemistry. She was the first woman to win a Nobel Prize and the only person to win Nobel Prizes in two different scientific fields (chemistry and physics). Curie’s work with radioactive elements revolutionized our understanding of the atomic world and laid the foundation for many modern technologies.
Chemistry is an exciting and essential branch of science that helps us understand the natural laws that govern the world around us. From the ancient Greeks to modern chemists like Marie Curie, people have been exploring the wonders of matter and using their knowledge to create new substances, develop medicines, and protect our environment. So, the next time you observe a color change or wonder how something works, remember that chemistry is the key to unlocking the secrets of the natural world.
Learn More: Parts of an Atom
Think of atoms as extremely tiny LEGO pieces that combine to create all the amazing things around us. We can’t even see them with our eyes only if we use special tools for scientists. Just like LEGO bricks have different colors and shapes, atoms come in various types. Some are called hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, and many others. Use the atom activities below to learn more.
Chemistry Activities You’ll Love
Bookmark this resource, 65 Amazing Chemistry Experiments for Kids, for incredible science experiments all year. Or try one of these favorites below.
Make Salad Dressing For Fun Chemistry
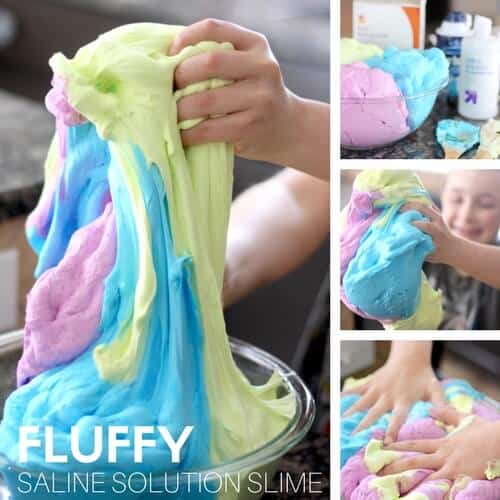
Set Up and Make Slime Chemistry Activities for Kids
Chocolate Science Reversible Change for Fun Chemistry!


Free Printable Chemistry Activities Guide
Are you ready to explore chemistry? Make sure to download this handy free printable Chemistry Activities Guide along with our science process worksheets.
Printable Science Projects For Kids
If you’re looking to grab all of our printable science projects in one convenient place plus exclusive worksheets and bonuses like a STEAM Project pack, our Science Project Pack is what you need! Over 300+ Pages!
- 90+ classic science activities with journal pages, supply lists, set up and process, and science information. NEW! Activity-specific observation pages!
- Best science practices posters and our original science method process folders for extra alternatives!
- Be a Collector activities pack introduces kids to the world of making collections through the eyes of a scientist. What will they collect first?
- Know the Words Science vocabulary pack includes flashcards, crosswords, and word searches that illuminate keywords in the experiments!
- My science journal writing prompts explore what it means to be a scientist!!
- Bonus STEAM Project Pack: Art meets science with doable projects!
- Bonus Quick Grab Packs for Biology, Earth Science, Chemistry, and Physics











